Matching People Across Surveillance Cameras
[/trx_title]
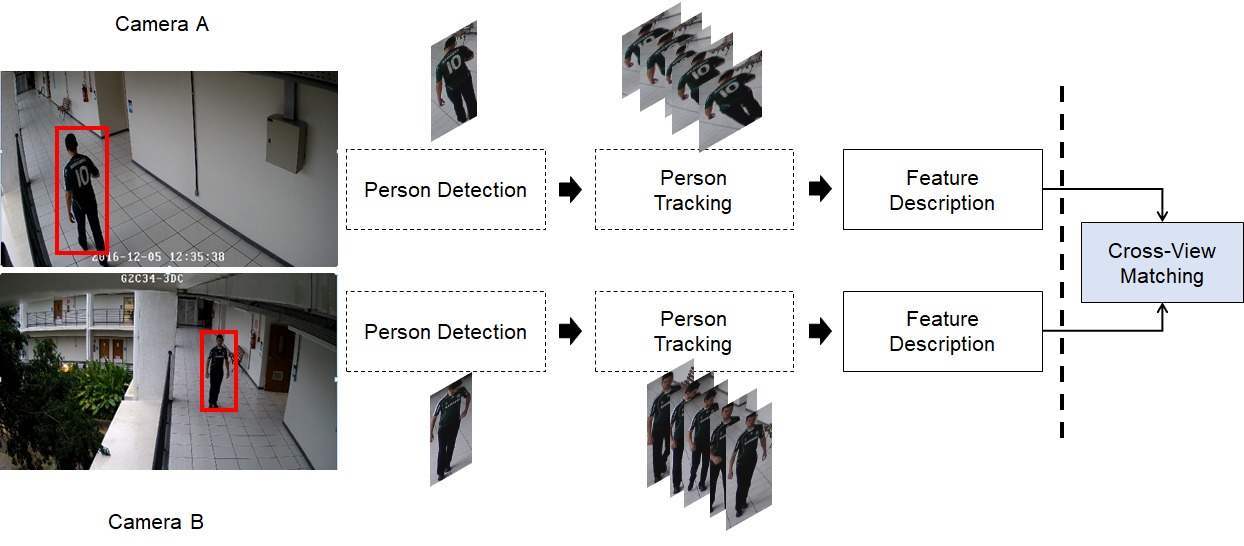
Raphael Felipe de Carvalho Prates, postdoctoral researcher and Smart Sense member, presented one of his works on Person Re-identification at the 2019 SIBGRAPI. The objective of Re-identification is determining if a person appearing in a camera A is the same appearing in a camera B at a different time, considering that the cameras’ field of view does not overlap. This is an important task for surveilling multi camera environments, where a broader monitoring (not limited to a single camera) of individuals is desired.
The contributions of this work are related to the manner in which the distances between the individuals captured by these two cameras are computed. The first one is Kernel Multiblock Partial Least Squares, which computes a common subspace for all cameras, and is scalable in relation to the number of cameras. The literature methods, in general, try to learn a subspace for each camera pair, which grows quadratically with the number of cameras. As a result, these methods are not scalable.
The second contribution is the Kernel Cross-view Collaborative Representation-based classification. This model was created to compute the distances between people captured by different cameras utilizing an auxiliary subset of individuals of which we have images in both cameras. The idea is that if a person X is similar to a person Y in a certain camera, they will continue to be similar regardless of the camera. Therefore, a mathematical formulation that solves the problem considering this restriction was proposed.